This is a summary of the paper "Evolutionary Optimization of Model Merging Recipes," which describes Sakana.ai's evolutionary model merging approach.
Introduction
The paper being summarized is:
- Published: March 19, 2024
- By: Sakana AI team
- Code: GitHub - SakanaAI/evolutionary-model-merge: Official repository of Evolutionary Optimization of Model Merging Recipes
All figures shown in this article are cited from the paper above.
Let's dive in.
Note: This article was translated from my original post.
Evolutionary Optimization of Model Merging Recipes
Overview
- Background
- Model merging is gaining attention as a cost-effective approach to building models.
- Challenge
- However, current model merging relies heavily on human intuition, experience, and domain knowledge—essentially a "black art."
- What they did
- Applied evolutionary algorithms to model merging.
- Combined approaches in both PS (parameter space/weights) and DFS (data flow space/layers).
- Conducted experiments using two approaches: merging Japanese-math reasoning models and creating a Japanese VLM model.
- Results
- Cross-domain model merging (Japanese model + math reasoning model) produced models with superior performance compared to existing models.
- Achieved results surpassing existing models on VLM tasks involving Japanese cultural context.
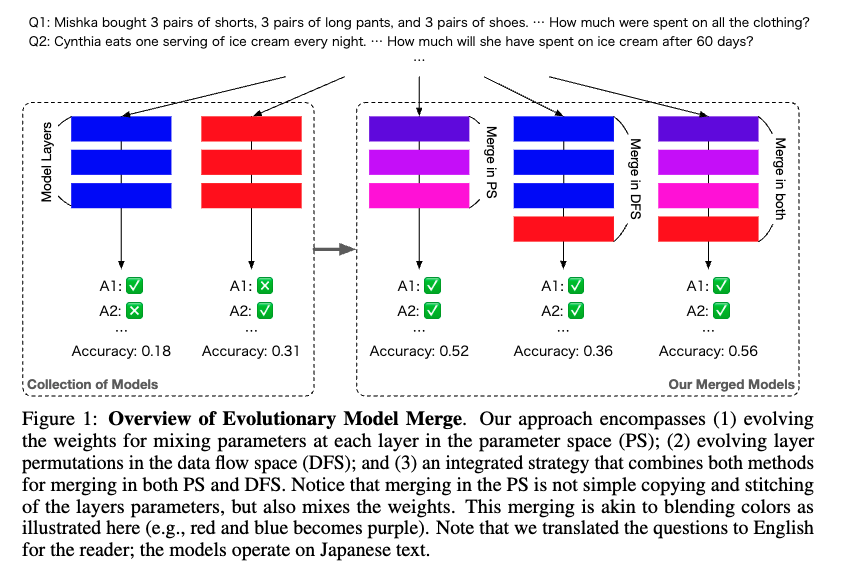
Method
- Performed merging at the PS (parameter space/weight level), DFS (data flow space/layer level), and a combination of both.
- Techniques used in PS merge
- TIES-Merging [2306.01708] TIES-Merging: Resolving Interference When Merging Models
- DARE [2311.03099] Language Models are Super Mario: Absorbing Abilities from Homologous Models as a Free Lunch
- Evolutionary algorithm used for optimization: CMA-ES The CMA Evolution Strategy: A Comparing Review | Springer Nature Link (formerly SpringerLink)
- Implementation: Optuna GitHub - optuna/optuna: A hyperparameter optimization framework
- Techniques used in DFS merge
- Combine layers using evolutionary algorithms
- While searching all possible combinations would result in an astronomical number of possibilities, preliminary investigation showed that reordering or repeating layers has negative effects, so these constraints narrowed the search space.
- When adjacent layers change, input variance changes, negatively affecting results. This is mitigated by multiplying by W to scale inputs. W is also optimized using evolutionary algorithms.
- Evolutionary algorithm used for optimization: CMA-ES
- Combining PS and DFS
- First perform PS merge, then use that merged model for DFS merge
Results
LLM Tasks

- MGSM-JA: Benchmark measuring mathematical reasoning ability in Japanese
- JP-LMEH: Benchmark measuring general Japanese language ability
- Source models for merging
- Model 1: Good at Japanese but poor mathematical ability
- Models 2, 3: Strong mathematical ability but weak Japanese ability → Poor MGSM-JA results
- Merged models
- Overall, results are better than source models
- Model 4 in particular, despite being created by merging models from different domains, demonstrates high performance
- PS merge is more effective than DFS merge
- Combining PS merge and DFS merge (Model 6) can further improve results (on MGSM-JA)
VLM Tasks

- JA-VG-VQA-500: Benchmark evaluating general VQA (Visual Question Answering) performance in Japanese
- JA-VLM-Bench-In-the-Wild: Benchmark evaluating complex VQA performance in the context of Japanese culture
- Both benchmarks were newly created by the authors for this study
- Merged models show higher performance than source models

Conclusion/Thoughts
That concludes my summary notes on the paper "Evolutionary Optimization of Model Merging Recipes."
Below are my personal thoughts:
- What are the authors trying to achieve?
- Automating and advancing model merging, which previously relied on human intuition, using evolutionary algorithms
- What are the key elements of the approach?
- Applying evolutionary algorithms to model merging
- What can I apply myself?
- Automated model merging is useful for those without abundant resources (GPU resources)
- What cited papers should I read next?
- Other thoughts
- While backpropagation probably doesn't occur in actual neural learning in the brain, something like model merging might. Perhaps learning in actual neural networks is a continuous merging process of models constructed within the brain. That's an exciting thought.
[Related Articles]